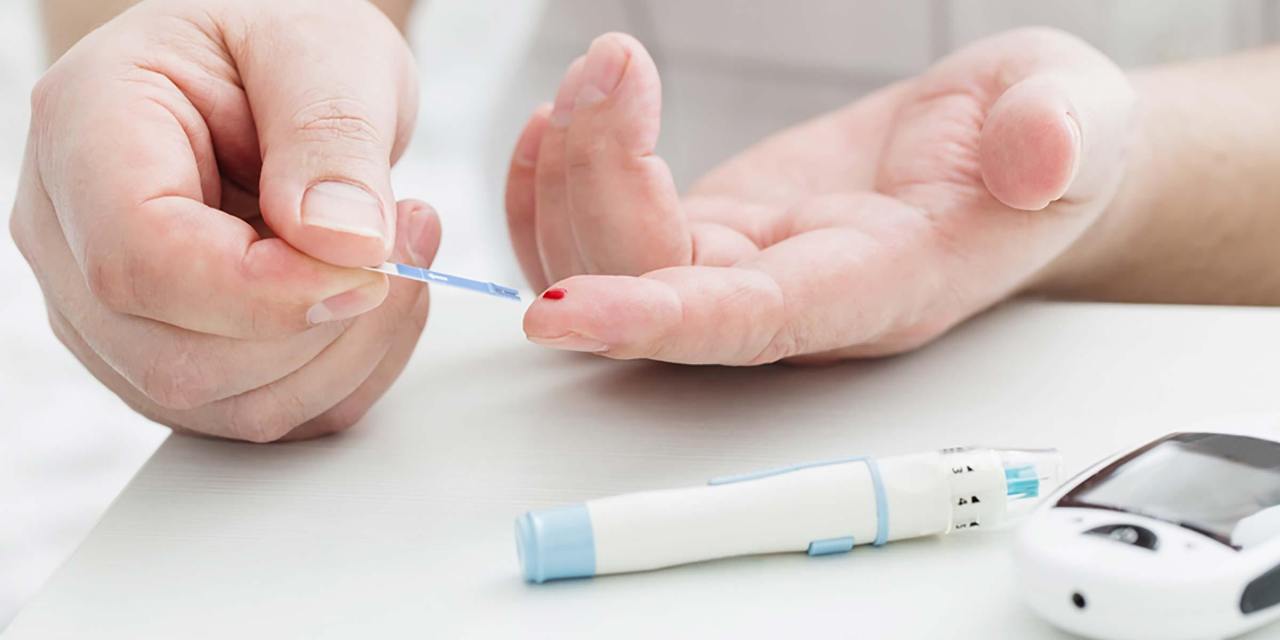
Diabetes mellitus is a disease that prevents your body from properly using the energy from the food you eat.
New York by Ed Hosseinipour Rph, CCo. Diabetes occurs in one of the following situations. The pancreas (an organ behind your stomach) produces little insulin or no insulin at all. Insulin is a naturally occurring hormone, produced by the beta cells of the pancreas, which helps the body use sugar for energy.
The pancreas makes insulin, but the insulin made does not work as it should. This condition is called insulin resistance.
Your body is made up of millions of cells. To make energy, the cells need food in a very simple form. When you eat or drink, much of your food is broken down into a simple sugar called glucose.
Glucose provides the energy your body needs for daily activities. The blood vessels and blood are the highways that transport sugar from where it is either taken in (the stomach) or manufactured (in the liver) to the cells where it is used (muscles) or where it is stored (fat). Sugar cannot go into the cells by itself.
The pancreas releases insulin into the blood, which serves as the helper, or the “key,” that lets sugar into the cells for use as energy.
When sugar leaves the bloodstream and enters the cells, the blood sugar level is lowered. Without insulin, or the “key,” sugar cannot get into the body’s cells for use as energy. This causes sugar to rise. Too much sugar in
There are two main types of diabetes

There are two main types of diabetes
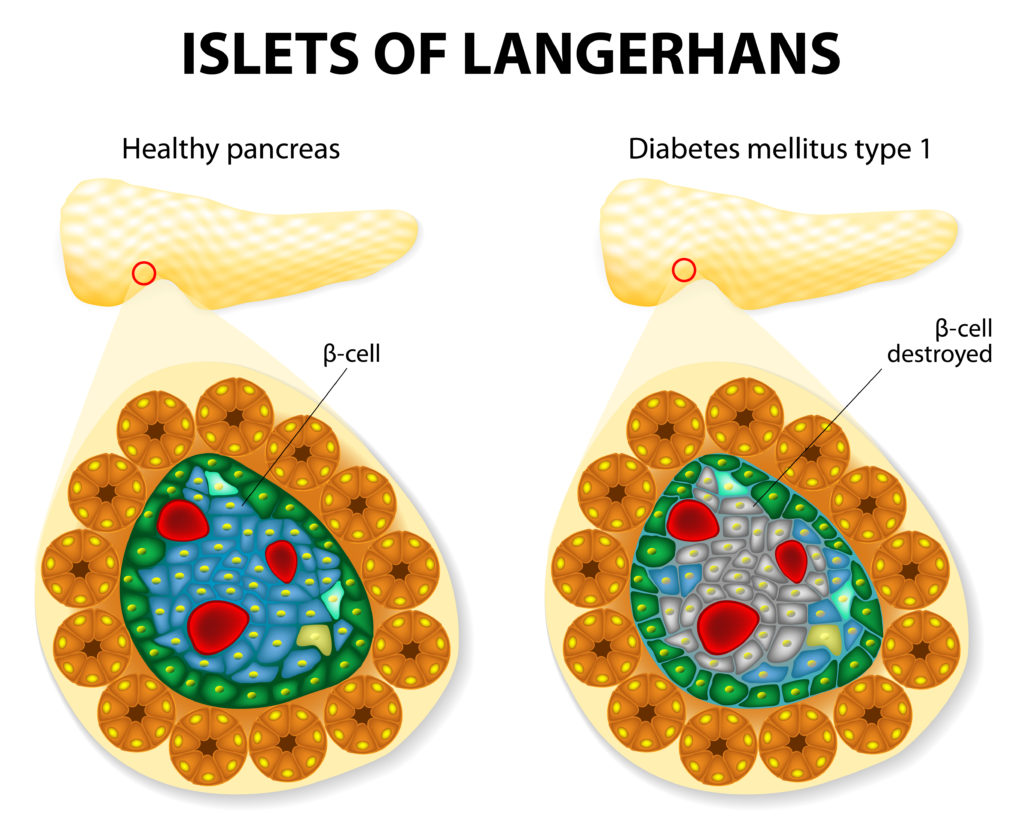
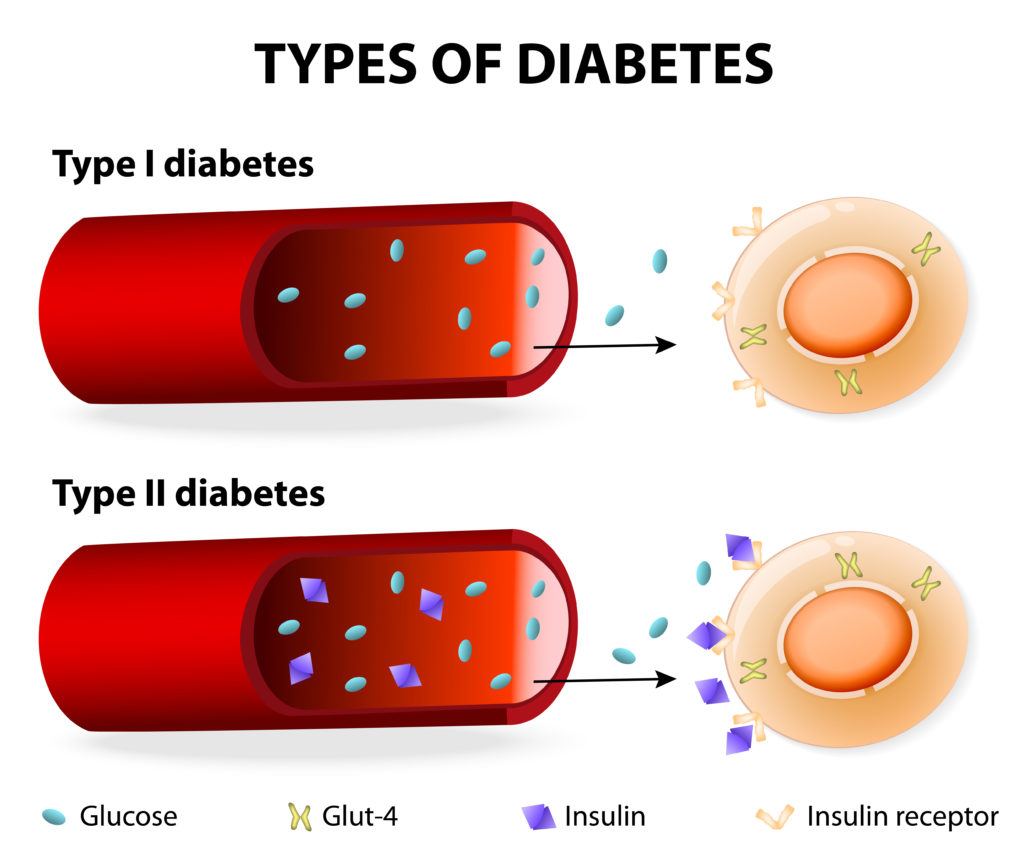
Type 1 diabetes: occurs because the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas (beta cells) are damaged. In type 1 diabetes, the pancreas makes little or no insulin, so sugar cannot get into the body’s cells for use as energy. People with type 1 diabetes must use insulin injections to control their blood glucose.

Type 1 is the most common form of diabetes in people who are under age 30, but it can occur at any age. Ten percent of people with diabetes are diagnosed with type 1.
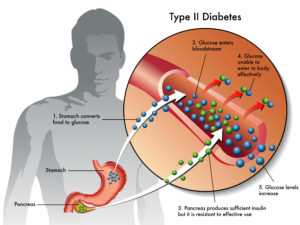
Type 2 diabetes (adult onset diabetes) The pancreas makes insulin, but it either doesn’t produce enough, or the insulin does not work properly. Nine out of 10 people with diabetes have type 2. This type occurs most often in people who are over 40 years old but can occur even in childhood if there are risk factors present.
- Type 2 diabetes may sometimes be controlled with a combination of diet, weight management and exercise. However, treatment also may include oral glucose-lowering medications (taken by mouth) or insulin injections (shots).
Other types of diabetes might result from pregnancy (gestational diabetes), surgery, use of certain medicines, various illnesses and other specific causes.
Causes of diabetes The causes of diabetes are not known. The following risk factors may increase your chance of getting diabetes, Family history of diabetes, African-American, Hispanic, Native American, or Asian-American race, Pacific Islander or ethnic background, Being overweight, Physical stress (such as surgery or illness), Use of certain medications, including steroids
- Injury to the pancreas (such as infection, tumor, surgery or accident), Autoimmune disease, High blood pressure ,Abnormal blood cholesterol or triglyceride levels, Age (risk increases with age) Smoking, History of gestational diabetes
It is important to note that sugar itself does not cause diabetes.
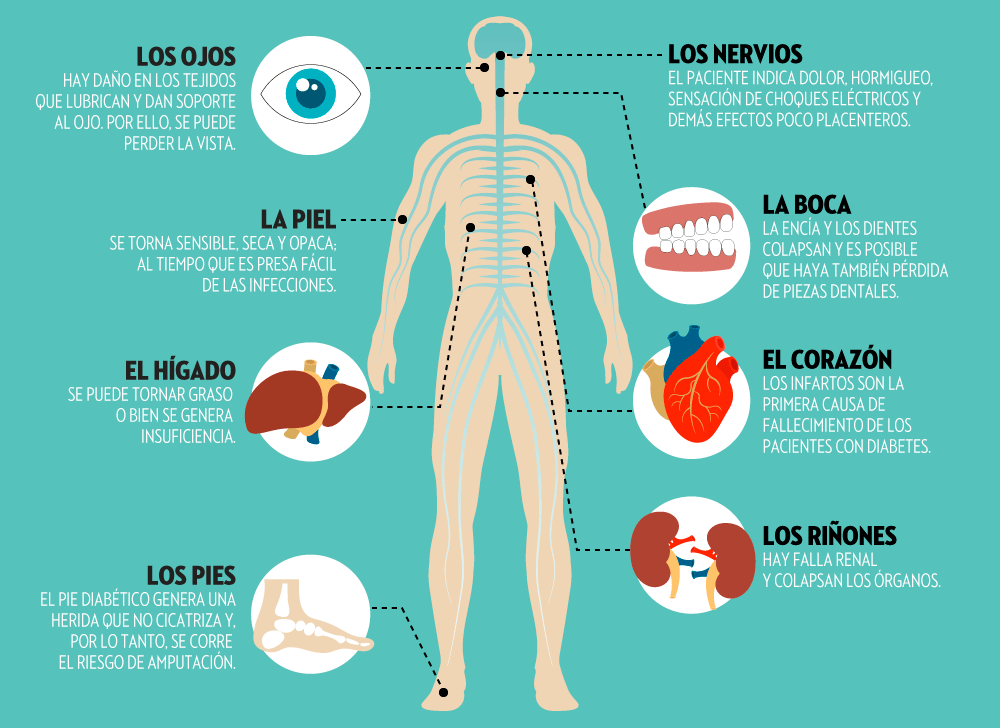
Symptoms of diabetes: The symptoms of diabetes include. Increased thirst, Increased hunger (especially after eating), Dry mouth, Frequent urination, Unexplained weight loss (even though you are eating and feel hungry), Weak, tired feeling, Blurred vision, Numbness or tingling in the hands or feet, Slow-healing sores or cuts, Dry and itchy skin, Frequent yeast infections or urinary tract infection
Diagnosis. There are different tools used to diagnose diabetes.
- Glycated hemoglobin (A1C) test.This blood test indicates your average blood sugar level for the past two to three months. Normal levels are below 5.7 percent, and a result between 5.7 and 6.4 percent is considered prediabetes. An A1C level of 6.5 percent or higher on two separate tests means you have diabetes. A1C levels need to be checked between two and four times a year
- Random blood sugar test. A blood sample will be taken at a random time and may be confirmed by repeat testing. Blood sugar values are expressed in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L). Regardless of when you last ate, a random blood sugar level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher suggests diabetes, especially when coupled with any of the signs and symptoms of diabetes, such as frequent urination and extreme thirst.
- Fasting blood sugar test. A blood sample will be taken after an overnight fast. A fasting blood sugar level less than 100 mg/dL (5.6 mmol/L) is normal. A fasting blood sugar level from 100 to 125 mg/dL (5.6 to 6.9 mmol/L) is considered prediabetes. If it’s 126 mg/dL (7 mmol/L) or higher on two separate tests, you have diabetes.
Treatment for type 1. Diabetes includes, Taking insulin, Carbohydrate, fat and protein counting, Frequent blood sugar monitoring, Eating healthy foods, Exercising regularly and maintaining a healthy weight
Treatment of type 2. Diabetes includes, Weight loss, Healthy eating, Regular exercise, Possibly, diabetes medication or insulin therapy, Blood sugar monitoring

Baron Specialty Pharmacy caries all types of diabetic medications including oral and injectables. Baron Pharmacy offers free diabetic testing and screening along with one on one consultation. We are proud to be a part of community educators and hope to make a difference in this and many other disease states within the Latino community. Please feel free to make an appointment for a free consultation with our specialty pharmacists. [ENG]
