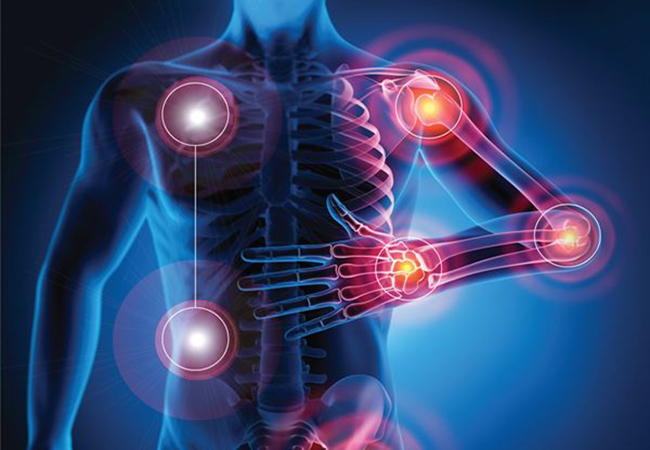
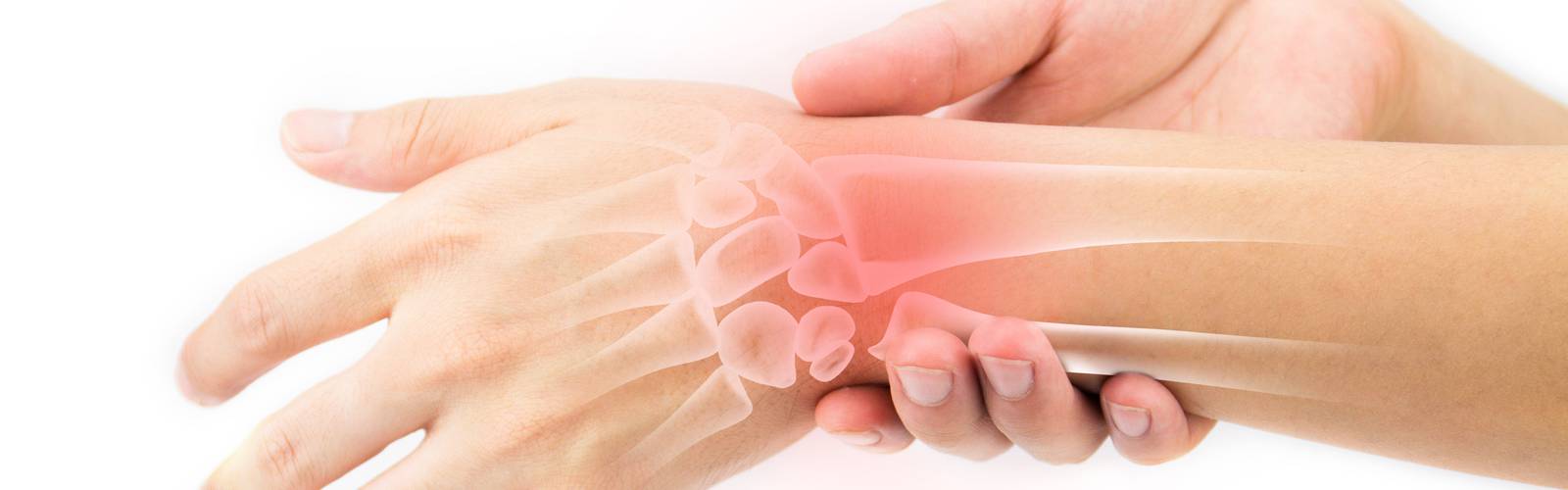
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system – which normally protects its health by attacking foreign substances like bacteria and viruses – mistakenly attacks the joints
New York, by Ed Hosseinipour, Specialty Pharmacist. This creates inflammation that causes the tissue that lines the inside of joints(Synovium) to thicken, resulting in swelling and pain in and around the joints. The synovium makes a fluid that lubricates joints and helps them move smoothly.
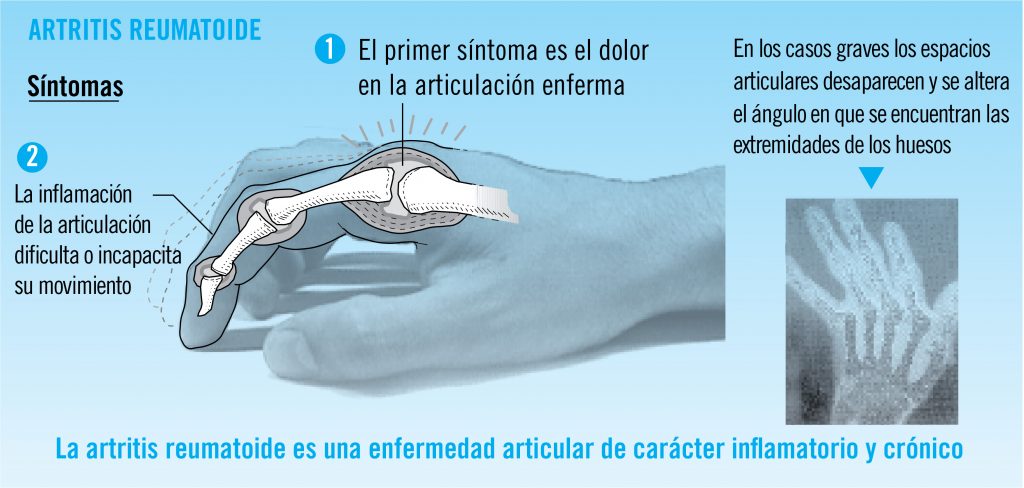
If inflammation goes unchecked, it can damage cartilage, the elastic tissue that covers the ends of bones in a joint, as well as the bones themselves. Over time, there is loss of cartilage, and the joint spacing between bones can become smaller. Joints can become loose, unstable, painful and lose their mobility. Joint deformity also can occur. Joint damage cannot be reversed, and because it can occur early, early diagnosis and aggressive treatment to control RA is recommended.
Rheumatoid arthritis most commonly affects the joints of the hands, feet, wrists, elbows, knees and ankles. The joint effect is usually symmetrical. That means if one knee or hand if affected, usually the other one is, too. Because RA also can affect body systems, such as the cardiovascular or respiratory systems, it is called a systemic disease. Systemic means “entire body.
” About 1.5 million people in the United States have rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Nearly three times as many women have the disease as men.
Causes: The cause of RA is not yet fully understood, although doctors do know that an abnormal response of the immune system plays a leading role in the inflammation and joint damage that occurs. No one knows for sure why the immune system goes awry, but there is scientific evidence that genes, hormones and environmental factors are involved.
Diagnosis: Your regular doctor may order blood tests and X-rays to help confirm a diagnosis. Or you may be sent to someone who specializes in diagnosing and treating RA. This type of doctor is called a rheumatologist.
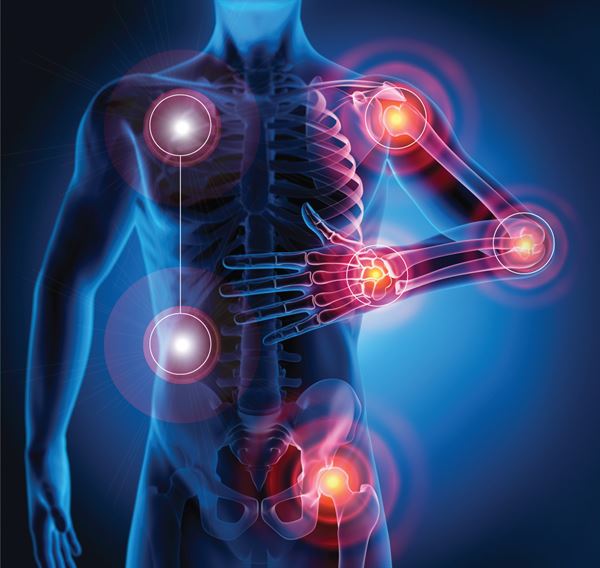
Symptoms:
- Joint pain, tenderness, swelling or stiffness for six weeks or longer
- Morning stiffness for 30 minutes or longer
- More than one joint is affected
- Small joints (wrists, certain joints of the hands and feet) are affected
- The same joints on both sides of the body are affected
Ongoing high levels of inflammation can cause problems FOR THE FOLLOWING ORGANS:
- Eyes. Dryness, pain, redness, sensitivity to light and impaired vision
- Mouth. Dryness and gum irritation or infection
- Skin. Rheumatoid nodules – small lumps under the skin over bony areas
- Lungs. Inflammation and scarring that can lead to shortness of breath
- Blood Vessels. Inflammation of blood vessels that can lead to damage in the nerves, skin and other organs
- Blood. Anemia, a lower than normal number of red blood cells
Treatment: Doctor usually follow these strategies:
Early, aggressive treatment. The first strategy is to reduce or stop inflammation as quickly as possible – the earlier, the better.
Targeting remission. Doctors refer to inflammation in RA as disease activity. The ultimate goal is to stop it and achieve remission, meaning minimal or no signs or symptoms of active inflammation. One strategy to achieve this goal is called “treat to target.”
Tight control. Getting disease activity to a low level and keeping it there is what is called having “tight control of RA.” Research shows that tight control can prevent or slow the pace of joint damage.
Medications

Drugs that ease joint pain and stiffness include:
- Anti-inflammatory painkillers, like aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen
- Pain relievers that you rub on your skin
- Corticosteroids, like prednisone
- Narcotic pain relievers
DMARDs. An acronym for disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, DMARDs are drugs that work to modify the course of the disease. Traditional DMARDs include methotrexate, hydroxycholorquine, sulfasalazine, leflunomide, cyclophosphamide and azathioprine.
Biologic response modifiers are manmade versions of proteins in human genes. They’re an option if your RA is more severe, or if DMARDs didn’t help. You might even take a biologic and a DMARD together. The doctor could also give you a biosimilar. These new drugs are near-exact copies of biologics that cost less.
Biologics approved for RA include: Abatacept (Orencia),
- Adalimumab (Humira), adalimumab-atto (Amjevita), Anakinra (Kineret), Certolizumab (Cimzia), Etanercept (Enbrel), etanercept-szzs (Erelzi), Golimumab (Simponi and Simponi Aria), Infliximab (Remicade), infliximab-dyyb (Inflectra), Rituximab (Rituxan), Sarilumab (Kevzara), Tocilizumab (Actemra), Tofacitinib (Xeljanz)
Steroids. For severe RA or when RA symptoms flare, your doctor may recommend steroids to ease the pain and stiffness of affected joints. In most cases, they can be used temporarily to calm a symptom flare

Baron Pharmacy encourages a positive outlook. Having a network of friends, family members and co-workers , also relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing, and most importantly exercise such as low-impact aerobics, muscle strengthening and flexibility can go a long way in the treatment.
Baron Pharmacy carries all regular and specialty medications prescribed for Rheumatoid Arthritis. It is our pride to be able to help our community in understanding and the treatment in many disease states including RA. Please feel free to call and arrange a personal consultation with a specialty pharmacist at Baron Specialty Pharmacy.[ENG]
