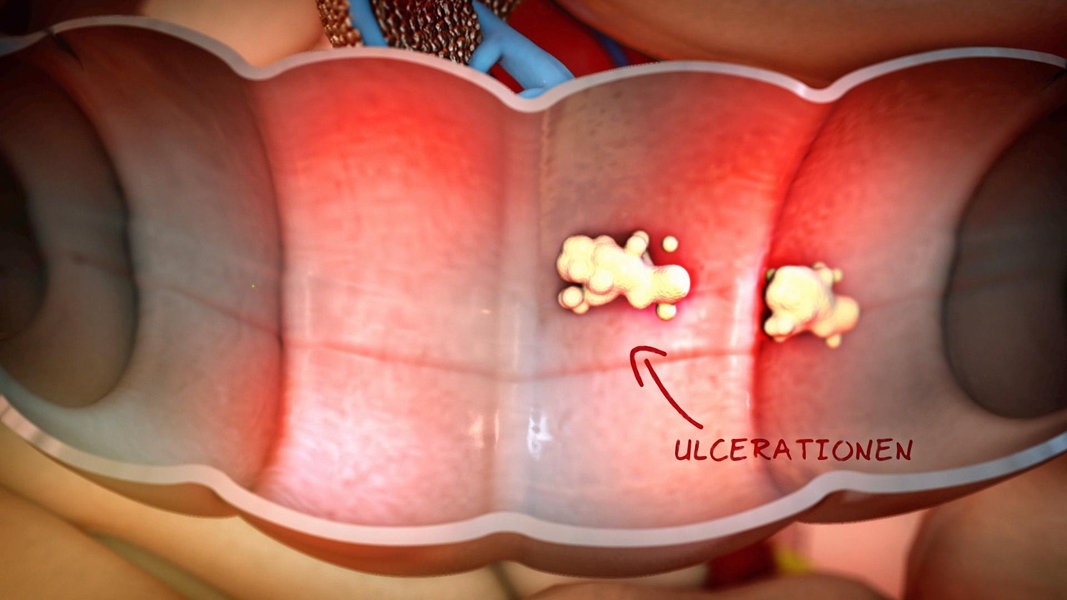
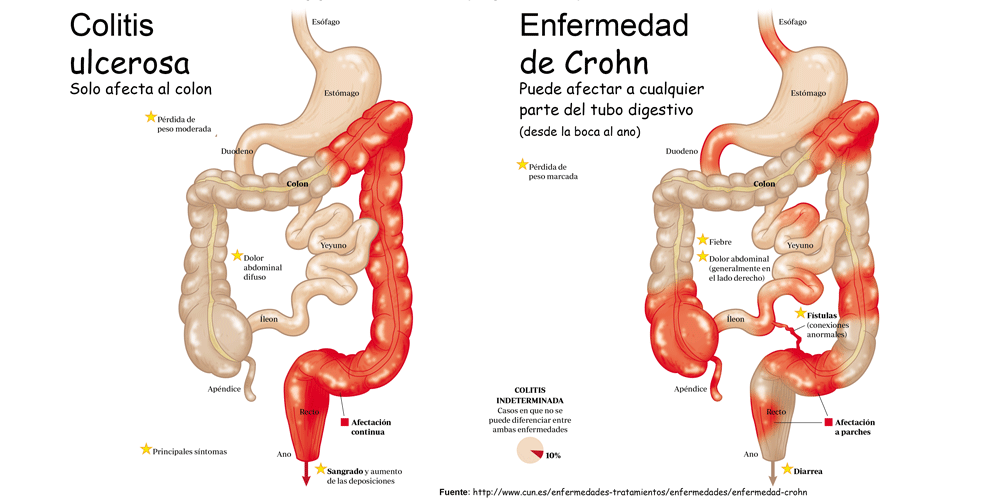
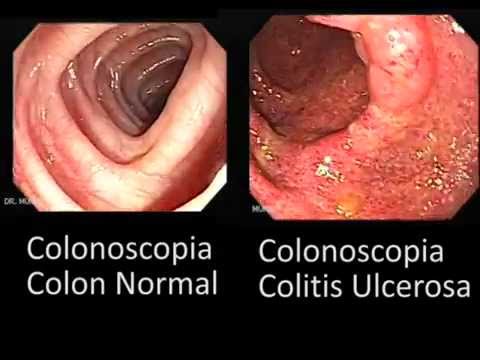
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic disease of the large intestine, also known as the colon, in which the lining of the colon becomes inflamed and develops tiny open sores, or ulcers, that produce pus and mucous.
New York by Ed Hosseinipour, Specialty Pharmacist The combination of inflammation and ulceration can cause abdominal discomfort and frequent emptying of the colon. Crohn’s disease belongs to a group of conditions known as inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory condition of the gastrointestinal tract.
Ulcerative colitis is the result of an abnormal response by your body’s immune system. Normally, the cells and proteins that make up the immune system protect you from infection. In people with IBD, however, the immune system mistakes food, bacteria, and other materials in the intestine for foreign or invading substances. When this happens, the body sends white blood cells into the lining of the intestines, where they produce chronic inflammation and ulcerations.

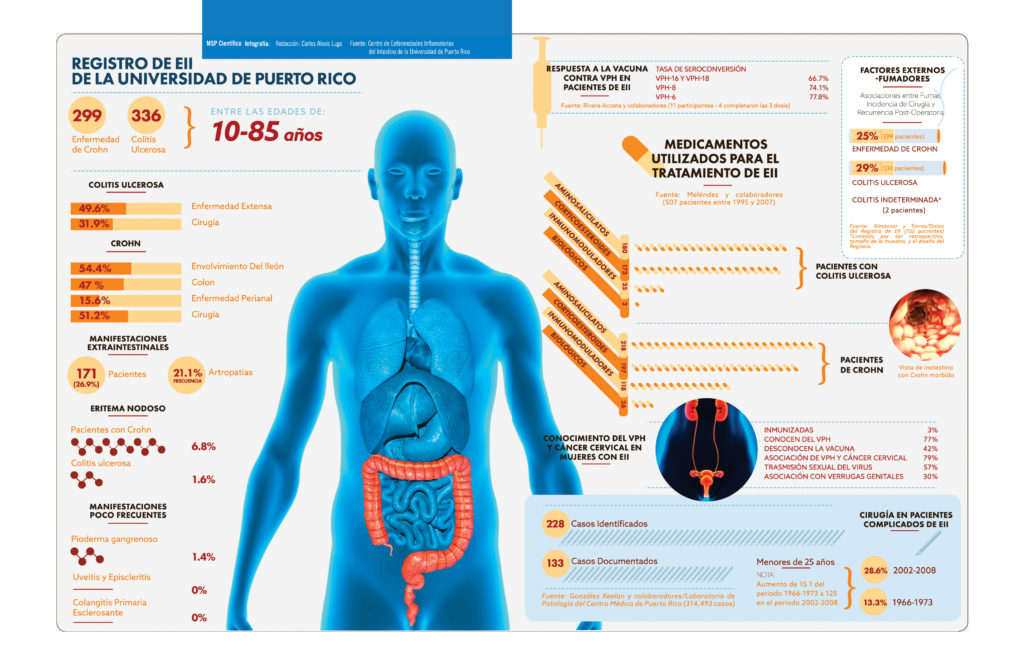
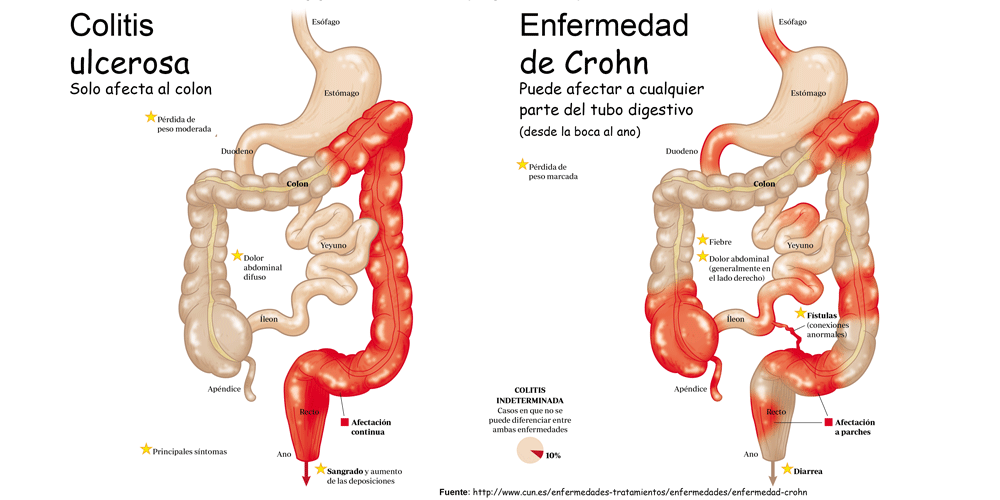
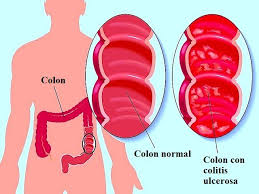
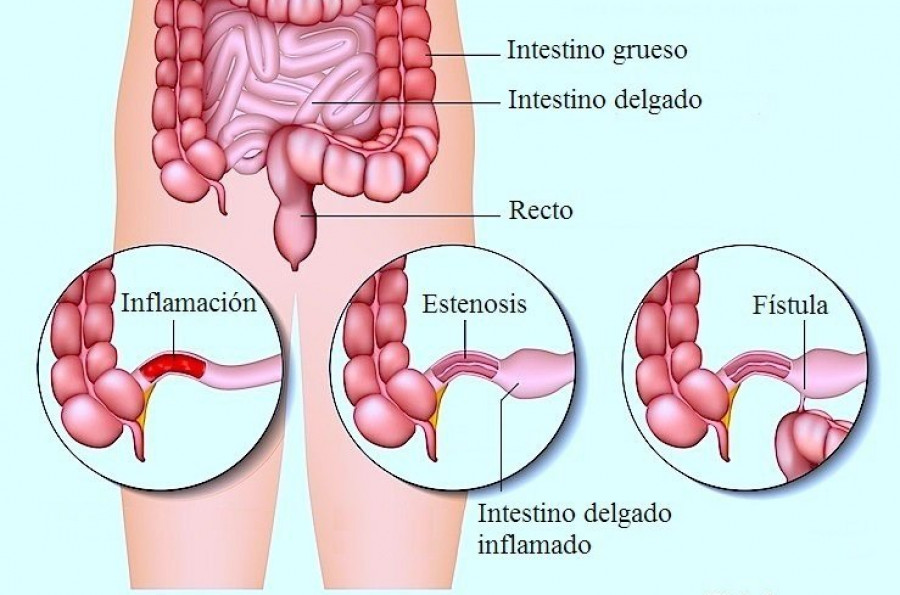
It’s important to understand the difference between ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. Crohn’s disease can affect any part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, but ulcerative colitis affects only the colon. Additionally, while Crohn’s disease can affect all layers of the bowel wall, ulcerative colitis only affects the lining of the colon.
Signs and Symptoms About half of all patients with ulcerative colitis experience mild symptoms. Be sure to consult your doctor if you experience any of the following symptoms, bowel movements become looser and more urgent, persistent diarrhea accompanied by abdominal pain and blood in the stool stool is generally bloody, crampy abdominal pain, People suffering from ulcerative colitis often experience loss of appetite and may lose weight as a result. A feeling of low energy and fatigue is also common. Among younger children, ulcerative colitis may delay growth and development.
Causes
Causes for Ulcerative and Crohn’s disease involves a complex interaction of factors: the genes the person has inherited, the immune system, and something in the environment. Foreign substances (antigens) in the environment may be the direct cause of the inflammation, or they may stimulate the body’s defenses to produce an inflammation that continues without control. many scientists to believe that ulcerative colitis may be the result of an interaction of a virus or bacterial infection of the colon and your body’s natural immune system response
. Normally, your immune system will cause temporary inflammation to combat an illness or infection, and then the inflammation will be reduced as you regain health. In people with ulcerative colitis, however, this inflammation can persist long after your immune system should have finished its job.

Normally, your immune system will cause temporary inflammation to combat an illness or infection, and then the inflammation will be reduced as you regain health. In people with ulcerative colitis, however, this inflammation can persist long after your immune system should have finished its job.Researchers believe that once the IBD patient’s immune system is “turned on,” it does not know how to properly “turn off” at the right time. As a result, inflammation damages the intestine and causes the symptoms of IBD.
That is why the main goal of medical therapy is to help patients regulate their immune system better.
Treatment There are many ways of treating Ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. It is important that patients are seeking help from specialist professionals in treating this disease.
AMINOSALICYLATES They are mainly used to treat mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis and sometimes Crohn’s disease.
CORTICOSTEROIDS They are used as short-term treatments of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis flares because they reduce inflammation quickly,
IMMUNOMODULATORS They are often used as a long-term treatment for those with IBD
ANTIBIOTICS For complications of Crohn’s disease like abscesses (pockets of pus)
BIOLOGIC THERAPIES Biologic therapies (also known as biologics) are proteins that block the action of specific molecules in the body that are involved in causing inflammation. These medications are indicated for people with a moderately to severely active form of IBD who have not responded well to other types of medications, or for those who are at high risk of complications from the disease. Biologics can be delivered through injection or intravenously (depending on the medication being used).
Baron Specialty Pharmacy is proud to offer regular free assessments for specialty patients. Feel free to contact us for much more helpful information.
This is where Baron Specialty Pharmacy can make a difference. We carry a wide variety of related medications and specialize in the specialty medications patients may need which are normally not available in regular pharmacies. It is much wiser to seek help in the treatment of special condition from a Specialty Pharmacy such as Baron Specialty Pharmacy .[ENG]